What Are Comprehensive Check-Ups?
Comprehensive check-ups include a series of tests and medical evaluations designed to monitor an individual’s health status. A standard check-up typically consists of:
- Medical history: A conversation with a doctor about your health, lifestyle, dietary habits, physical activity, family medical history, and any possible symptoms.
- Physical examination: Assessment of basic health indicators such as blood pressure, pulse, temperature, weight, and height.
- Laboratory tests: Blood count, blood sugar levels, lipid profile (cholesterol), liver and kidney function tests, hormone analyses, and urinalysis.
- Diagnostic methods: If necessary, these may include ultrasound, ECG, X-rays, mammograms, or other specialized examinations.
Why Undergo a Comprehensive Check-Up?
Unhealthy habits such as poor diet, stress, smoking, and lack of physical activity significantly contribute to various health issues. The rising prevalence of conditions like high blood pressure, diabetes, obesity, and elevated cholesterol levels can lead to severe vascular damage, heart attacks, heart failure, or strokes. Alarmingly, these risk factors often develop silently and unnoticed over months or even years and are frequently detected during comprehensive check-ups.
Furthermore, the success of treatment and prognosis for malignant diseases, such as prostate, breast, uterine, colon, stomach, or lung cancer, largely depends on early detection. These conditions often develop insidiously, without prominent symptoms. By the time symptoms appear, it might be too late for effective treatment. Besides genetic predisposition, lifestyle, diet, physical (in)activity, smoking, and chronic conditions influence the risk of developing cancer. Regular check-ups allow for early identification of changes, such as PSA level assessments for men, breast ultrasounds for women, or specific diagnostic procedures for individuals with a family history of cancer.
Prevention: The Most Cost-Effective Investment in Health
Prevention is always better and more cost-effective than treatment. Regular check-ups enable the early recognition of risks and diseases, preventing complications that require expensive and complex medical interventions. For instance:
- Timely detection of high cholesterol can prevent atherosclerosis and heart issues.
- Early diagnosis of changes in the breast or prostate is often treatable using minimally invasive methods with high success rates.
A comprehensive check-up is not an expense but an investment in health and quality of life.
Advantages of Comprehensive Check-Ups
- Early Disease Detection
Most serious diseases, such as cancer, diabetes, and cardiovascular conditions, do not show symptoms in their early stages. Comprehensive check-ups allow their detection when treatment is most effective and less invasive. - Monitoring Chronic Conditions
For individuals with chronic conditions like diabetes, hypertension, or asthma, regular check-ups help evaluate the effectiveness of therapy and adjust treatment plans. - Prevention and Education
In addition to physical examinations, doctors provide education on a healthy lifestyle, the importance of proper nutrition, regular physical activity, and avoiding harmful habits like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. - Time and Cost Savings
Prevention is always less demanding, faster, and cheaper than treating diseases in advanced stages. Early problems often require simpler therapies. - Mental Health
Comprehensive check-ups address not only physical health but also assess mental well-being. Doctors can recognize signs of stress, anxiety, or depression and recommend appropriate steps.
Specific Tests by Age and Gender
- Children and Adolescents: Regular check-ups to monitor growth, development, and vaccinations. Special attention is given to detecting vision, hearing, and posture problems.
- Women: Gynecological exams, Pap smears, mammograms after age 40, and tests related to hormonal changes and pregnancy.
- Men: Prostate exams after age 50, testosterone level checks, and specific tests based on risks (e.g., cardiovascular diseases).
- Older Adults: Focus on preventing heart diseases, osteoporosis, cognitive disorders, and age-specific cancers.
How Often Should We Have a Comprehensive Check-Up?
The recommended frequency of check-ups varies:
- Individuals under 40 years: Every 2-3 years, unless specific health concerns exist.
- Individuals aged 40-65 years: Annually, especially if risk factors such as family history of illness or an unhealthy lifestyle are present.
- Over 65 years: Annually or as advised by a doctor.
How to Prepare for a Comprehensive Check-Up
- Bring medical documentation: If you have previous diagnoses, lab results, or a list of medications, take them with you.
- Be honest with your doctor: Transparency about symptoms, lifestyle, and medical history is crucial for an accurate diagnosis.
- Follow instructions: If advised to come fasting or avoid certain activities before the check-up, adhere to these guidelines for reliable results.
Comprehensive Check-Up Packages
We offer three types of comprehensive check-up packages for women:
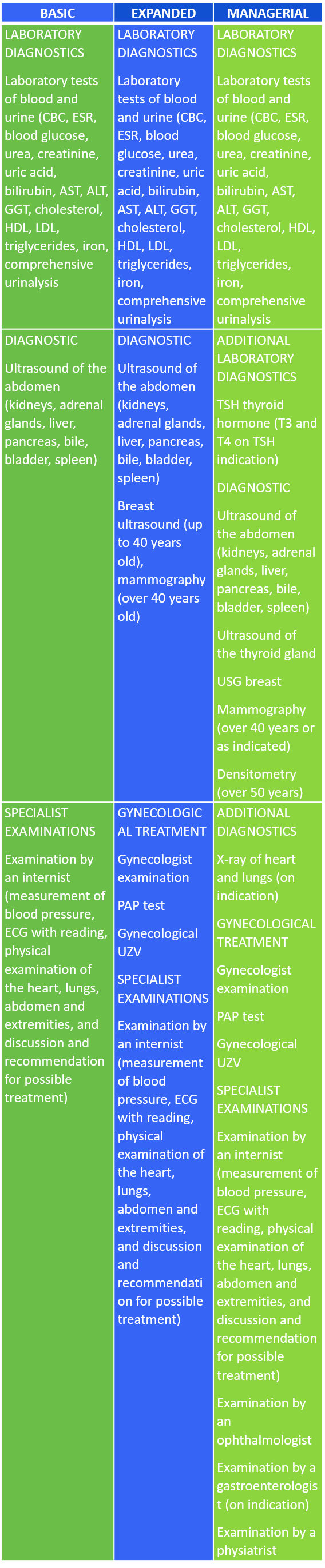
Likewise, we differentiate three types of comprehensive check-up packages for men:
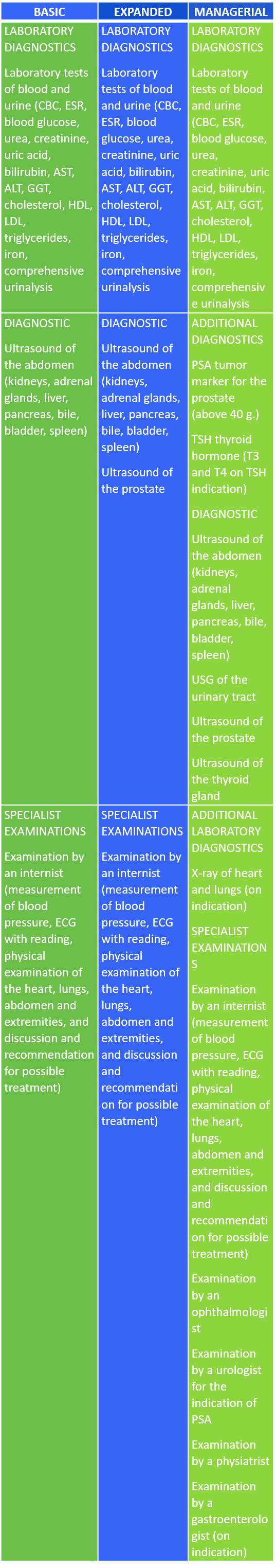
In addition to the basic check-up, some of the additional services included in extended and managerial check-ups are consultations with an ophthalmologist and a gastroenterologist.
Beyond these exams, it is important to emphasize why regular monitoring of tumor markers is essential.
What Are Tumor Markers?
Tumor markers are specific substances produced by the body's cells in response to the presence of malignant tumors or, in some cases, benign conditions. Measuring these markers in blood, urine, or other body fluids provides valuable information for early detection, monitoring, and evaluating the success of cancer treatment.
Regular monitoring of tumor markers can save lives, as many types of cancer show no symptoms in their early stages. Early detection significantly increases the chances of successful treatment.
Tumor Markers in Women
Women are particularly advised to monitor markers associated with gynecological cancers, which are among the most common malignant diseases in the female population.
Key tumor markers for women include:
- CA-125 – Used to detect and monitor ovarian cancer. Elevated levels may indicate disease presence, though benign conditions like endometriosis can also increase levels.
- CEA (Carcinoembryonic Antigen) – Used to monitor various cancers, including colorectal and breast cancer.
- CA 15-3 and CA 27-29 – Specific markers for monitoring breast cancer, especially in later stages or when assessing recurrence.
- HE4 (Human Epididymal Protein 4) – Used alongside CA-125 to improve accuracy in detecting ovarian cancer.
- Alpha-Fetoprotein (AFP) – Assists in diagnosing tumors during pregnancy and some rare ovarian tumors.
Regular testing of these markers is especially important for women with a family history of malignancies or those at increased risk due to hormonal changes, lifestyle factors, or other variables.
Tumor Markers in Men
In men, tumor markers are used for the early detection of specific cancers and to monitor the effectiveness of treatment.
Key tumor markers for men include:
- PSA (Prostate-Specific Antigen) – Critical for early detection of prostate cancer. Elevated PSA levels may indicate cancer or benign prostate conditions like enlargement or inflammation (prostatitis).
- CEA – Monitors colorectal cancer and cancers of the lung, pancreas, and stomach.
- Alpha-Fetoprotein (AFP) – Used to diagnose testicular tumors and some liver cancers.
- Beta-HCG (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin) – Helps diagnose certain testicular tumors.
- LDH (Lactate Dehydrogenase) – A nonspecific marker for testicular tumors and useful for monitoring disease progression.
Regular monitoring of these markers is particularly recommended for men over 50 and younger men with a family history of prostate or testicular cancer.
Why Is Regular Monitoring of Tumor Markers Important?
Routine monitoring of tumor markers is crucial for the early detection of malignant diseases, often before the first symptoms appear. This enables timely treatment initiation and significantly increases the chances of recovery.
For patients already diagnosed with tumors, tumor markers play a vital role in tracking treatment success and identifying potential recurrence. For individuals at increased risk of developing specific cancers, such as those with genetic predispositions or family histories, regular marker testing helps mitigate more severe consequences.
Additionally, marker results allow doctors to tailor therapy to a patient’s specific needs, enhancing treatment effectiveness.
Comprehensive Check-Ups: Your Investment in Health
Regular comprehensive check-ups are not just an obligation but an investment in your health and quality of life. Their importance cannot be overstated – early disease detection, prevention of complications, and empowering individuals to make healthy decisions are key benefits that impact both life expectancy and quality.
Don’t wait for problems to arise; take control of your health today and schedule your comprehensive check-up!
